Sell Farm Complete Guide to Selling a Farm Successfully
Selling a farm is not just about transferring land ownership; it often involves assets, buildings, equipment, and even the community connected to it. The process can be complex, requiring collaboration between farm owners, potential buyers, real estate agents, and sometimes legal authorities.
Unlike selling a home, where buyers focus mainly on location and amenities, selling a farm requires deeper considerations. Buyers look at soil fertility, irrigation systems, production potential, and long-term profitability before making decisions.
Key Factors That Influence Farm Value
The value of a farm depends on several critical factors. First, soil quality plays a major role. Fertile soil with a reliable irrigation system commands higher prices than less productive land.
Location is another key factor. Farms located near distribution hubs, highways, or urban centers usually attract more buyers. On-site infrastructure, such as barns, storage facilities, and worker housing, also adds to the property’s overall value.
Legal and Financial Considerations in Selling a Farm
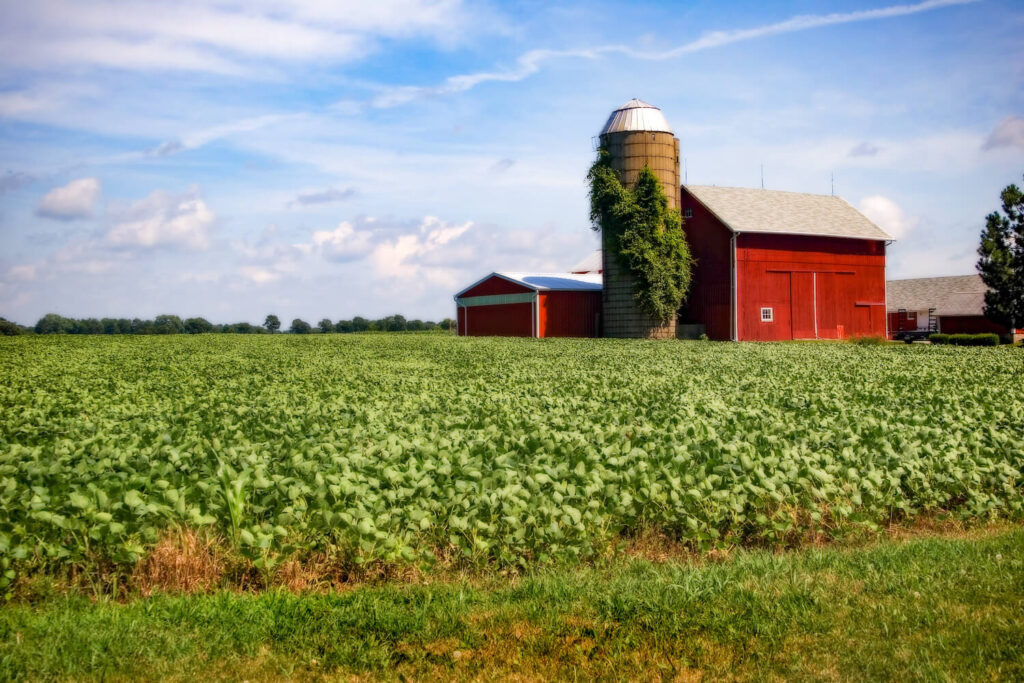

Legal documentation is essential in selling farmland. Title deeds, land-use permits, and environmental clearances must be prepared before putting the property on the market. Without proper documentation, the sale process may face delays or even cancellation.
Financially, sellers should prepare clear records of farm income. Crop yields, operational costs, and profit margins are important to demonstrate the farm’s investment potential. A well-documented financial history increases buyer confidence.
Real-World Examples of Farm Sales
Example 1: Midwestern Grain Farm
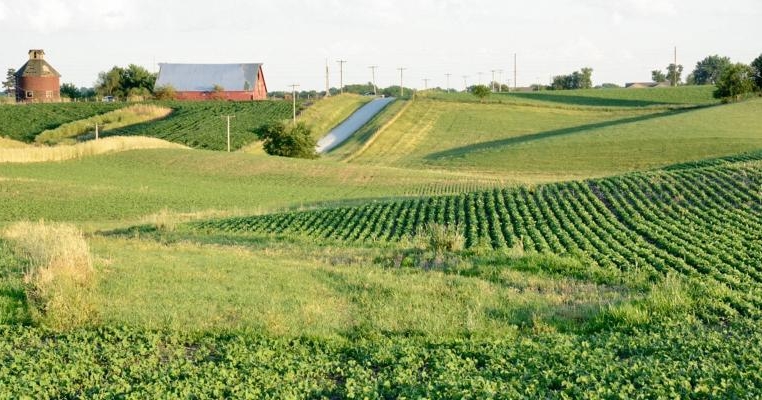

A grain farm in the Midwest, United States, was sold at a premium due to its fertile soil and proximity to major distribution routes. Buyers were also impressed by the use of modern farming technology that improved efficiency and yield.
This case shows how location, soil quality, and technology integration can significantly increase a farm’s market value.
Example 2: Dairy Farm with Modern Facilities
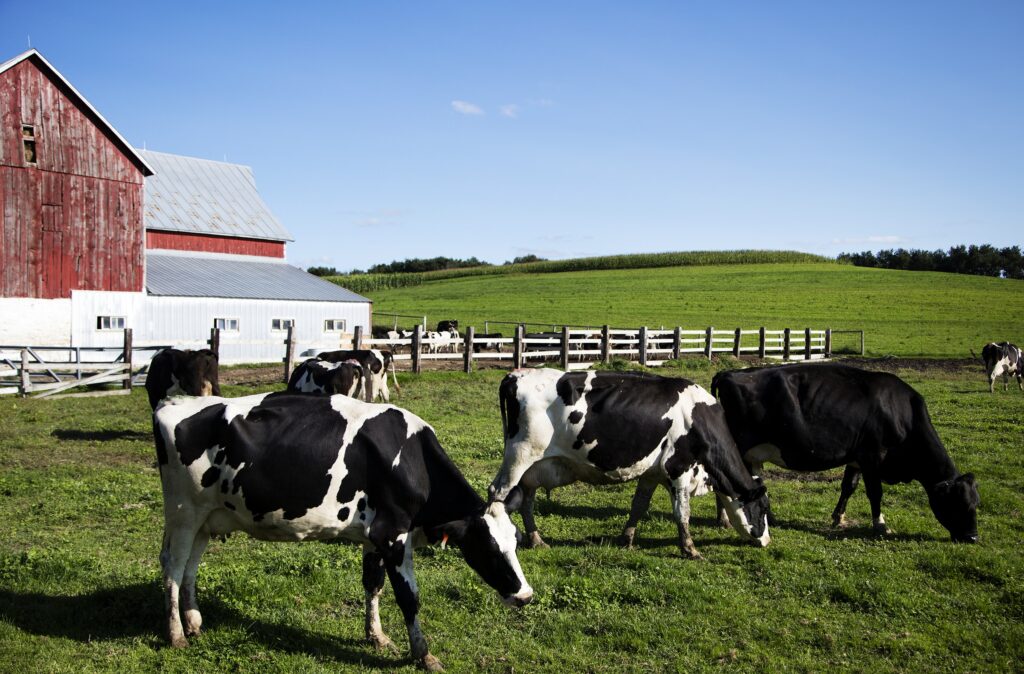

In Europe, a dairy farm sold quickly thanks to its modern facilities, including automated milk cooling systems and large storage barns. Additionally, the farm had long-term contracts with dairy companies, offering guaranteed revenue streams for the buyer.
Having ready-to-use infrastructure and business agreements made this farm far more attractive compared to empty farmland.
Example 3: Organic Vegetable Farm
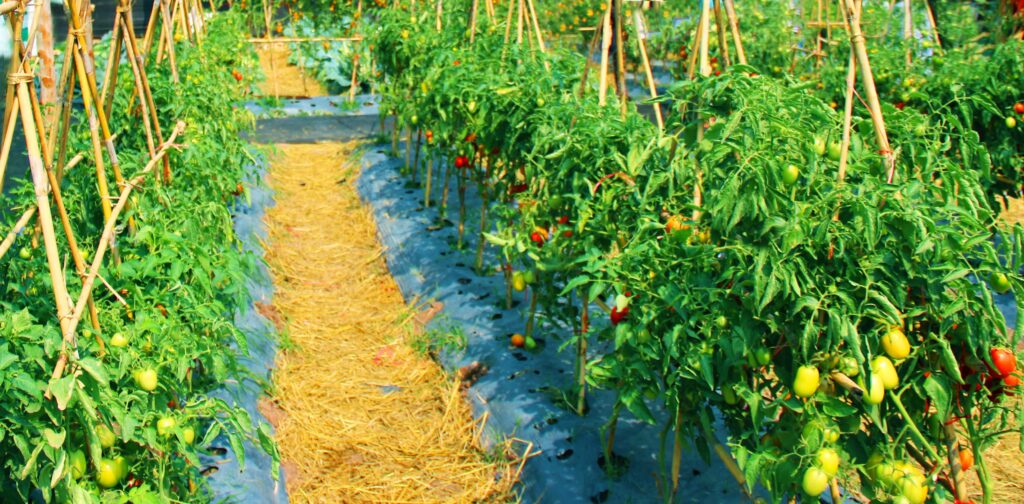

An organic vegetable farm in Asia was sold at a higher-than-expected price due to its established reputation in organic produce. The farm held organic certification and had built a loyal customer base, making it a valuable asset beyond just the land itself.
This example proves that branding, certification, and reputation can increase a farm’s sale value just as much as land size or crop output.
Benefits of Using Technology in Selling a Farm
Technology has transformed the farm-selling process. Drones, for example, can capture aerial photos and promotional videos, providing potential buyers with a detailed view of the property without an initial site visit.
Online property listing platforms also widen the pool of potential buyers. Instead of relying only on local markets, sellers can reach investors worldwide. Digital tools streamline negotiations, provide transparency, and save time for both parties.
Practical Use Cases of Selling a Farm
Solving Inheritance Disputes
Farms are often sold due to inheritance issues. When heirs cannot agree on who should manage the land, selling the farm becomes the fairest solution, allowing the proceeds to be divided equally.
Transitioning into Retirement
Many farm owners decide to sell their farms upon retirement. The sale provides financial stability and a retirement fund, often representing the biggest asset they own.
Expanding or Shifting Business Ventures
Selling a farm can also be a strategic move to invest in a larger or more profitable property. Farmers may sell their current land to purchase better farmland closer to markets or with higher productivity potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What factors determine the selling price of a farm?
The main factors include soil quality, location, available infrastructure, production potential, and well-documented financial records.
2. Does technology really speed up farm sales?
Yes. Tools like drones, digital marketing, and online listing platforms allow sellers to showcase their farms more effectively, reaching wider audiences and reducing delays.
3. What are common mistakes in selling a farm?
The biggest mistake is failing to prepare complete legal and financial documents. Without these, buyers may hesitate, leading to delayed or unsuccessful transactions.